India must “reform” its emissions Norms, called the corporate average fuel efficiency (cafe) framework, to align with global best practices by increasing protection me for Small Cars, a new study. Researchers at nomura has said.
The study said that India follows a linear weight-based approach under its cafe Norms, “Where a lower weight implies a more stringent target”. This, it said, was different from regulations in major automobile markets like the United States, China, European Union and Japan, Where Smaller, Lightweight Cars Have Relaxed Emissions Norms. In India, Companies Such as Market Leader Maruti Suzuki Have Been Lobbying In Favor of Relaxed Emission Norms For small Hatchback Cars, A Segment This is seeing declining sales.
“Globally, all major automotive markets including the us, china, japan, korea, and europe offer regulatory protection to small cars under their cafeworks due to their environment and succonomic Value.” The Nomura Researchers Said in the Recent Study.
“In Contrast, India’s Linear Weight-Based Cafe Approach Penalises Lighter Vehicles with Disproportionately Stringent Co₂ Targets. This creates a structural bias heavier with HIHHERS EMEVER EMEMY. Easily, While Cars with Lower Emissions Failing, A Key Decarbonization Strategy, “They added.
What are India’s Cafe Norms?
The Bureau of Energy Efficiency (Bee) Introduced The Cafe Norms in 2017 to Regulate Fuel Consumption and Carbon Empics from Passinger Vehicles. These Norms Apply to Vehicles Running on Petrol, Diesel, Liquefied Petroleum GAS (LPG), Completed Natural Gas (CNG), Hybrids, and Electric Vehicles (EVS) Weighing Less Thans 3500 Kg. The Norms were tightened in the beginning of the financial year 2022-23, with an increasing penalies for non-aliens.
Designed to Reduce Oil Dependency and Curb Air Pollution, The Cafe Norms Push Automakers to Lower Carbon Dioxide Easy Wile Incementing the Production of EVS, HYBRIDS, And CNG VEHICALS, WHICH ARE Carbon-Intensive than Cars that run on fossil fuels.
For 2022-23, the bee, under the union ministry of power, required car companies of all units solving the year to Achieve India’s corporate Average Fuel Efficiency (CAF) Norms. This meant a fuel consumption of not more than 4.78 liters per 100 km and carbon dioxide emissions of not more than 113 grams per km (Since it has a direct correlation with the Amount of Fuel consume).
Story Continues Below this ad
Nomura Researchers Said that under India’s emissions Calculation System, The Cafe Framework gives Heavier Vehicles More Rexed Absolute Co₂ Limits. A LARGE SUV or Premium Car is allowed a Much Highr Co₂ Target Whereas small Cars get a much more stringent target.
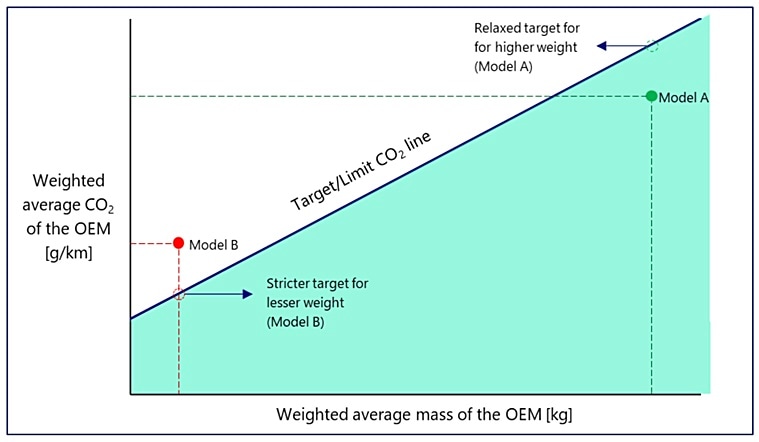
The Graph Above, Prepared by Nomura Researchers, shows that one of the high-spelling suvs (represented with a green dot, model a), hasd co₂ emissions of about 10g/km, is also a Highering. CAR (represented with a red dot, model b) having co₂ emissions of about 100g/km is non-alplish.
“One of the Common Strategies OEMs Use to Lower Co₂ Emisions is Reducing Vehicle Weight While Mainting the safety characteristic of the vehicle. Absolute CO₂ IF Lightweighting, it is a result, as a result. Lightweighting, especially for already light, entry-level cars, “The study said.
How other markets temper Norms for small cars
The researchers cited examples of the USA, China, Japan, South Korea and European Union to show that these markets, regulators have prescribed emissions norms for Smaller Cars.
Story Continues Below this ad
USA: Follows a pieceWise linear approach for cars below a certain footprint, which encases that the target something not keep on increasing indefinitely. This implies that fuel economy target below cler footprint is fixed and does not become programively stricter with further Roduction in size, encourse comparately relaxed taraxed tarages for cars.
China: Follows a similar piecewise linear approach, for cars buck a Certain Curb Weight Threshold, The Target becomes Constant, which encases that the fuel consumption Target Does not keep on teep on teep on teep. Lighter Cars.
South korea: For cars below a Certain Curb Weight, The Fuel Economy Target Mains Constant, Entering That Smaller, Lighter Cars are not subjected to increasingly stricter targets as weight reedhes. Further, manufacturers also get an additional adventage of 5-7g/km in their cafe performance, basically on the sales ratio of small cars in their portfolio.
Japan: Japan Follows A Non-Linear Approach, Entering That Small Light-Weight Cars Are Subjected To Disproporttionately Higher Targets.
Story Continues Below this ad
Europe: It has gone a step ahead and made the slop negative (-0.0144) which means bigger cars have a low absolute co₂ Target and small cars have relaxed taragets.
